INNOVATIONS AND RESEARCH
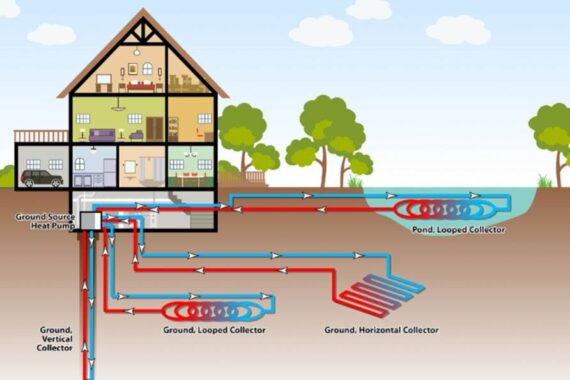
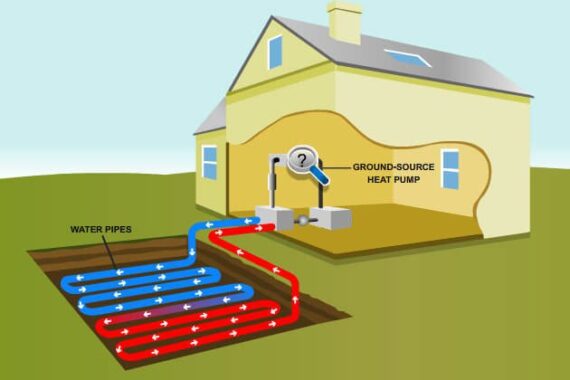
NREL researchers are working to improve the characterization and proliferation of geothermal heat pumps (GHP) technologies through techno-economic analysis, market modeling, and barriers analysis. GHPs, also referred to as ground-source heat pumps or geo-exchange, can reduce energy use, carbon emissions, and peak electricity demand in buildings while satisfying space heating, space cooling, and domestic water heating needs. A GHP system is composed of a ground heat exchanger, one or more water-source heat pumps, and systems for air and water distribution.
GHPs use the thermal mass in the shallow subsurface of the ground as the heat sink/source for heat pump operation. The ground temperature at about 30 ft below the surface at a given location is constant. This undisturbed ground temperature differs by location, but it typically ranges from 40°F to 70°F in the United States. The small difference between ground temperature and desired room temperature (around 70°F) makes GHPs very energy efficient for space cooling and heating as well as water heating. Thus, GHP systems are among the most widespread green technologies for heating and cooling buildings.